Jenkins: Difference between revisions
m (→Jobs) |
m (Add links to the actual page declaring the steps to setup phabricator or new jenkins jobs) |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
== Phabricator == | == Phabricator == | ||
[https://wiki.softwareheritage.org/wiki/Debian_packaging#Setting_up_the_repository_on_Phabricator Setting up the repository to trigger debian package] | |||
== New swh module jenkins job == | |||
[https://wiki.softwareheritage.org/wiki/Debian_packaging#Setting_up_the_Jenkins_jobs Setting up a new swh module jenkins job] | |||
[[Category:Software development]] | [[Category:Software development]] | ||
Revision as of 13:11, 23 September 2020
Jenkins
The CI is run by Jenkins on jenkins.softwareheritage.org
Authentication
Software Heritage staffers can login via the Jenkins Web user interface using the same personal *nix credentials they use to login into other machines.
Jobs
There are 2 categories of job:
- jobs related to jenkins itself, like running Jenkins Job Builder, updating and managing docker images. These are found in the jenkins-tools directory.
- jobs dedicated to testing/building swh packages.
Jobs definition
Most of the jobs are created using Jenkins Job Builder (aka JJB).
The source repository is https://forge.softwareheritage.org/source/swh-jenkins-jobs/
Each time a new revision is pushed on this repo, the JJB job is executed. This job updates already existing jobs or create new ones (if any). Beware not to break the JJB job!
Job execution environments
Jenkins job execution may occur either on the Jenkins master node directly (typically for jenkins-tools jobs), or in a docker jenkins slave.
Docker images used by Jenkins are created and updated using the Dockerfiles in
https://forge.softwareheritage.org/source/swh-jenkins-dockerfiles/
For now, there are 2 different images:
- swh-jenkins/tox: a Debian stretch with python3 and tox installed; used to run unit tests; it's available in Jenkins under the label swh-tox
- swh-jenkins/sphinx: based on the former tox image, it adds everything needed to compile the documentation with sphinx; it's available in Jenkins under the label swh-sphinx.
swh packages
Each swh package has a Jenkins Folder in which are all the jobs dedicated to this package.
There are two jenkins jobs for each swh package:
- Phab. Diff (here for swh-core): these jobs are executed each time a Phabricator Diff is created or updated,
- master branch (here for swh-core): these jobs are executed when git revisions are pushed on the master branch.
When these jobs are started by Phabricator, the job's end status is pushed back on the Phabricator object that triggered the build (ie. the Diff object or the Revision object). As a result, the build status for a given Diff or git revision will be displayed in the forge.
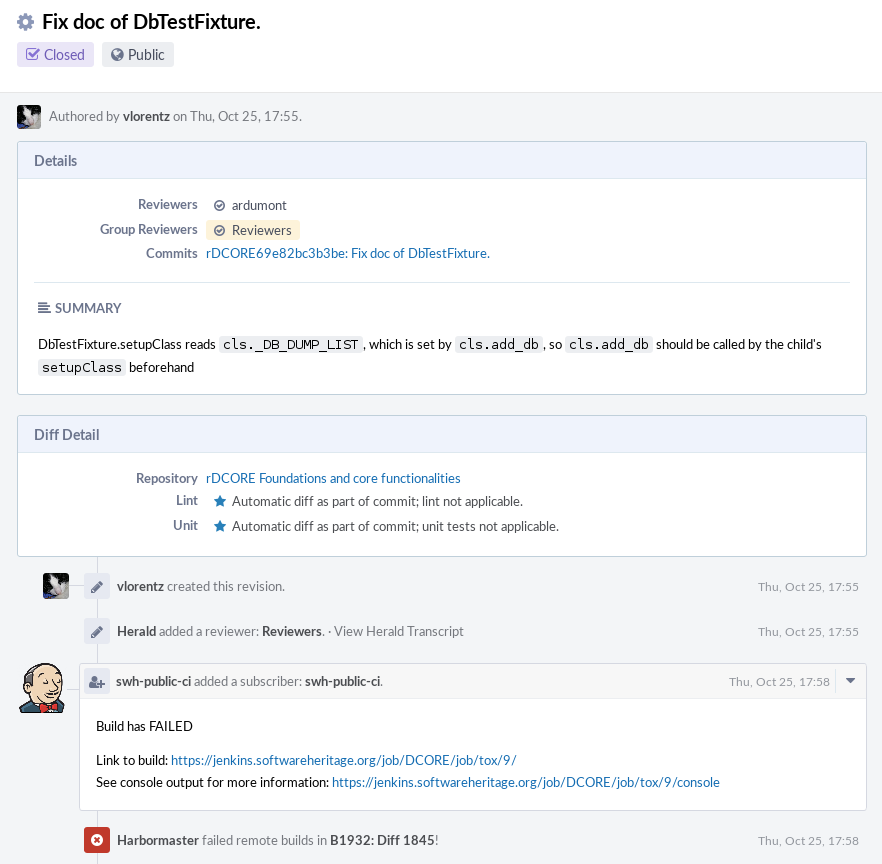
The Diff in Phabricator will typically look like:
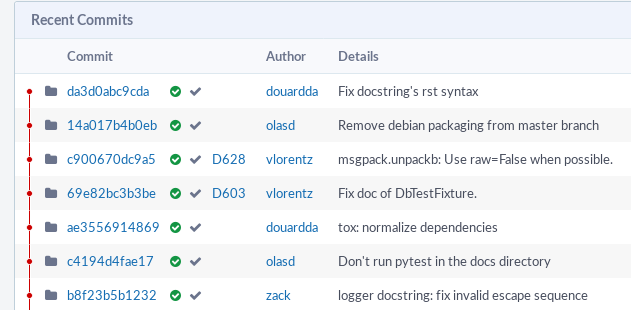
The Diffusion view of a git repository will look like:
where the green "checks" in each revision means the CI passed OK on this revision.
Dashboards and metrics
The swh dashboard gives a global view on the CI status of swh packages. It shows all the "master branch" job status for all swh packages, as well as a few metrics for these builds (%success, code coverage, execution time, etc.)
Starting a job manually
You should be able to execute any job by hand. When logged in, on the job's description page (eg. swh-core master) you should be able to push the "Build with Parameters" button which opens a form where you can specify the job's input parameters.
Note that you can also restart a (generally failed) job. From the job execution summary (eg. this execution) you may find a "Restart from Stage" button (on "master branch" jobs only) or a "Replay" button that will allow you to recreate a job with the same parameters as the original job execution.
Phabricator
Setting up the repository to trigger debian package