VPN: Difference between revisions
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
== Revoking a client certificate == | == Revoking a client certificate == | ||
On | On the firewall (master) [https://192.168.50.1]: | ||
* go to the [[https://192.168.50.1/system_crlmanager.php System / Trust / Revocation]] page | |||
* edit the "OpenVPN certificate revocation list" CRL | |||
[[File:Vpn-crl-list.png]] | |||
[ | |||
* go to the bottom of the page | |||
[[File:Vpn-csr-certificate.png]] | |||
* select the certificate to revoke | |||
* Add | |||
The counter of revoked certificate should be increased by one on for the OpenVPN CSR on the CSR list | |||
== /etc/hosts entries == | == /etc/hosts entries == | ||
Revision as of 10:23, 9 July 2021
The Software Heritage server and the VMs running on it are severely firewalled. To get onto their network unrestricted, a VPN based on OpenVPN is available.
The setup is client-server, with per-client certificates.
OpenVPN client configuration
Raw OpenVPN
Sample configuration file, e.g., /etc/openvpn/swh.conf:
remote vpn.softwareheritage.org ns-cert-type server comp-lzo nobind dev tun proto udp port 1194 log /var/log/openvpn.log up-restart persist-key persist-tun client ca /etc/openvpn/keys/softwareheritage-ca.crt cert /etc/openvpn/keys/softwareheritage.crt key /etc/openvpn/keys/softwareheritage.key user nobody group nogroup # If you are using resolvconf, add this: # Make sure you add louvre to /etc/hosts to avoid issues in using the vpn-provided DNS server. script-security 2 up /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf down /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf # If you want the connection to persist when your network fails, add this: ping-restart 10
In addition to the above configuration file, you will need to install the following 3 files under /etc/openvpn/keys (matching the paths within the sample above):
- softwareheritage-ca.crt: public certificate for the Software Heritage certification authority (CA)
- softwareheritage.crt: public, client-specific (certificate signed by the admin, see below)
- softwareheritage.key: private, client-specific key (generated by the user, see below)
Activate the openvpn server
as root, run
systemctl enable openvpn@swh.service systemctl start openvpn@swh.service systemctl status openvpn@swh.service
Note: Internally, the `swh` must match the /etc/openvpn/swh.conf filename.
Excerpt of a successful start:
root@machine:~# systemctl status openvpn@swh.service
openvpn@swh.service - OpenVPN connection to swh
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/openvpn@.service; indirect; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2020-12-17 19:03:29 IST; 22min ago
Docs: man:openvpn(8)
https://community.openvpn.net/openvpn/wiki/Openvpn24ManPage
https://community.openvpn.net/openvpn/wiki/HOWTO
Main PID: 12302 (openvpn)
Status: "Initialization Sequence Completed"
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915)
CGroup: /system.slice/system-openvpn.slice/openvpn@swh.service
└─12302 /usr/sbin/openvpn --daemon ovpn-swh --status /run/openvpn/swh.status 10 --cd /etc/openvpn --script-security 2 --config /etc/openvpn/swh.conf --writepid /run/openvpn/swh.pid
Dec 17 19:03:29 machine systemd[1]: Starting OpenVPN connection to swh... Dec 17 19:03:29 machine systemd[1]: Started OpenVPN connection to swh.
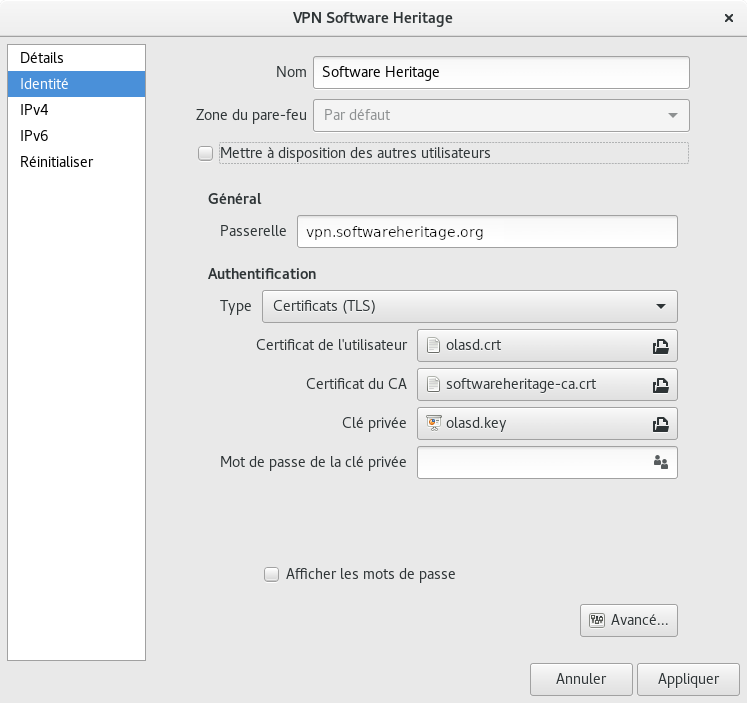
Network Manager GUI
You need network-manager-openvpn and network-manager-openvpn-gnome for the configuration gui.
Obtaining a client certificate
For users
Generate a keypair (key + certificate signing request) using the following command:
openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout openvpn.key -out openvpn.csr -subj "/CN=<your username>"
Please replace <your username> with something that uniquely identifies the certificate.
Make sure openvpn.key is stored in a safe place (it's your private key, which will allow anyone to connect to the VPN).
Provide the CSR file to a sysadmin through a reasonably authenticated medium.
For admins
- On the firewall (192.168.50.1), go to the System / Trust / Certificates page
- click on the add button on the upper right
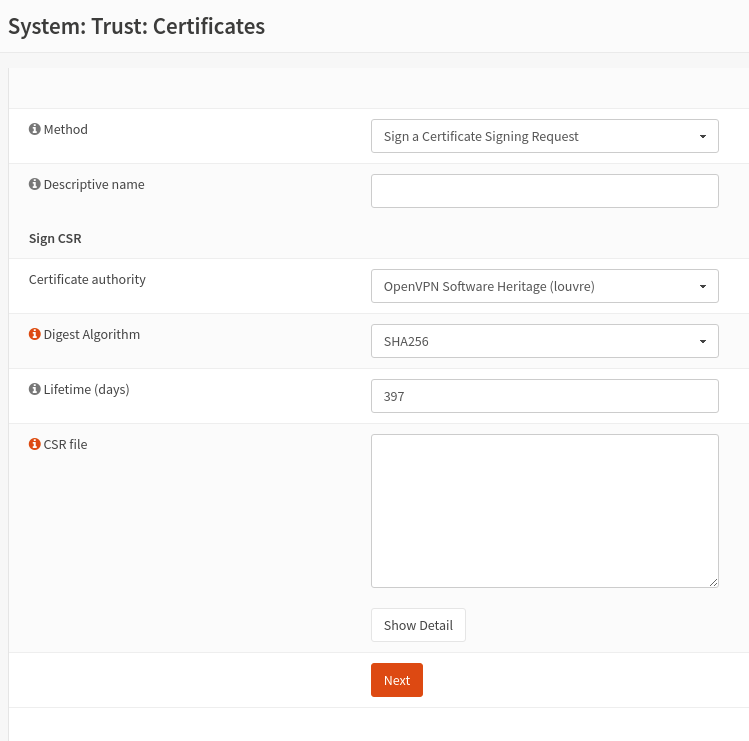
- On the Method list, choose "Sign a certificate Signing Request"
Fetch the CSR file provided by the user, for instance with scp USERNAME.csr louvre:
- Enter the user name on the descriptive name
- Select "OpenVPN Software Heritage (louvre)" as Certificate Authority
- Enter the duration, usually 10 years
- Paste the csr
- Validate
- check the details of the csr and validate
Revoking a client certificate
On the firewall (master) [1]:
- go to the [System / Trust / Revocation] page
- edit the "OpenVPN certificate revocation list" CRL
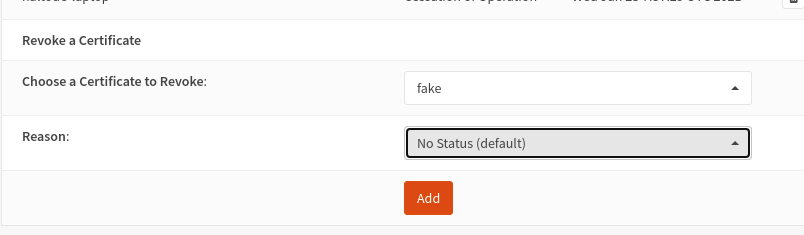
- go to the bottom of the page
- select the certificate to revoke
- Add
The counter of revoked certificate should be increased by one on for the OpenVPN CSR on the CSR list
/etc/hosts entries
Once the Vpn is setup on your machine, you can access Software Heritage hosts via their private IP addresses; see Network configuration.
OpenVPN now pushes the address of our DNS server (192.168.100.29, pergamon).
You might want to add louvre.softwareheritage.org in your /etc/hosts to avoid a bootstrap problem if the "on-vpn" DNS server is in your resolv.conf.